Capstan and Turret Lathe-Introduction, Working, Advantage, Difference
Capstan and Turret Lathe: Introduction: A Capstan and Turret machine is a creation machine. It is utilized to fabricate…
Table of Contents
Capstan and Turret Lathe:
Introduction:
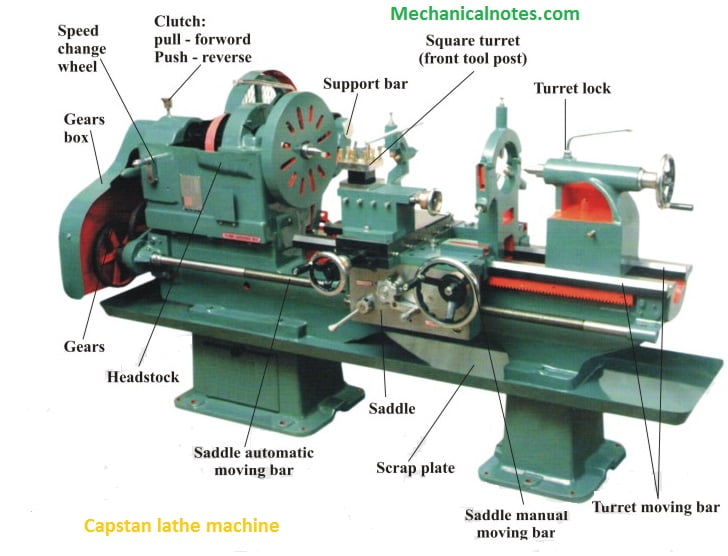
- A Capstan and Turret machine is a creation machine. It is utilized to fabricate any number of indistinguishable pieces in the base time.
- It was modified of engine lathes.
- They were first created in United State of America by PRATT and WHITNEY in 1860.
- Capstan and turret lathes are Semi-automatic lathes that help in making the Auxiliary motion quick and accurate.
- The Tail stock is replacing with an index able multi station tool head.
- It is a manufacturing process machine used for production of work piece.
- Turret head has a Hexagonal square having six appearances with a drag for mounting at least six than six instruments one after another. The threaded hole on these faces are using to hold the tools.
Brief working:
- The work piece is holding in collect or chucks which are actuating hydraulically or pneumatically. On the turret head, all the tools are holding in the respective holes.
- The tool is moving with the help of turret head, according to the sequence of operation.
- Drilling, boring, turning, reaming, threading tools are mounting on the turret head.
- Forming, Chamfering, Knurling tools are mounting on the front end of the turret.
- The Parting tool is mount in an inverted position on the rear end of the turret.
- The turret head is moving back to its initial position after completing each operation where indexes the tools automatically.
Advantages
- The production rate is high.
- Different ranges of speeds are obtained.
- A number of tools can be accommodated.
- Fewer skill operators are required hence lowers the labor cost.
- Higher rigidity so can withstand heavy loads.
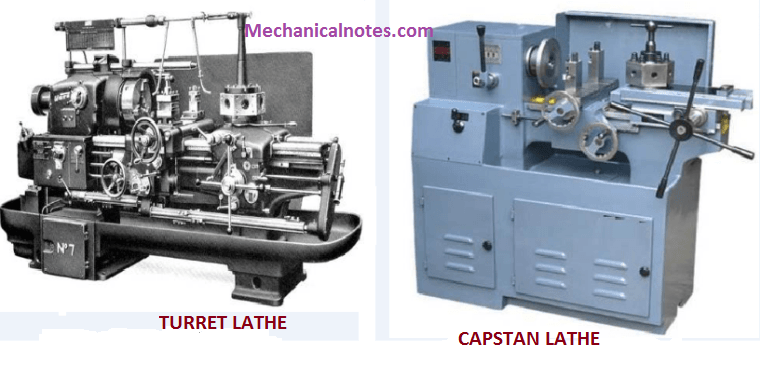
Difference Between Capstan and Turret lathe
| S. No. | Capstan lathe | Turret lathe |
| 1. | The turret head is mounted on the ram and the ram is mounted on the saddle. | The turret head is directly mounted on the saddle and the saddle slides over the bed ways. |
| 2. | The saddle is fixed during machining. | The saddle is moved along with the turret head during machining. |
| 3. | The turret head can’t be moved crosswise. | The turret head can be moved crosswise. |
| 4. | The lengthwise movement of turret is less. | The lengthwise movement of turret is more. |
| 5. | Maximum bar size is up to 60 mm. | Maximum bar size is up to 200 mm. |
| 6. | Collect is used to hold the work piece. | Jaw chuck used to hold the work piece. |
| 7. | Rate of tool feeding relatively faster. | Rate of tool feeding relatively slower. |
| 8. | It is a light weight machine. | It is a heavier machine. |
| 9. | It has a simple tool head. | It has hexagonal tool head. |
| 10. | Automatic indexing. | Manual indexing. |
Capstan and Turret Lathe Tools
1. Turning tool
2. Facing tool
3. Parting tool
4. Forming tool
5. Chamfering tool
6. Drilling
7. Boring tool
8. Counter bore
9. Reamer
10. External thread cutting tool
11. Internal thread cutting tool
12. Workstop
1. Turning tool

- Turning tool is mounted on the cross-slide or knee holder.
- Hollow mill is a special turning tool used in capstan and turret lathe.
2. Facing tool

- Facing tool may be mounted on the cross-slide or on the knee tool holder.
3. Parting tool
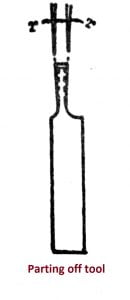
- The tool is mounted on the rear tool post.
- All round clearance is given on tool to clear the work while cutting.
4. Forming tool

- The forming tools may be straight or circular type.
5. Drill

- A drill is a tool primarily that use for making round holes or driving fasteners.
6. Boring tool

- The drilling apparatuses mounted on drilling bars are utilized for developing a gap in a capstan or turret machine.
7. Counter bore

- The counter bores are used for enlarging the drilled hole from one end.
8. Reamer

- The reamer are used for sizing and finishing a hole.
- Reamers may have at least two straight or helical woodwinds in the body.
9. External thread cutting tool

- External thread are cut on a job in a capstan or turret lathe by using any one of the following tools:
a. Solid button dies

b. Chasers

i. Radial chaser
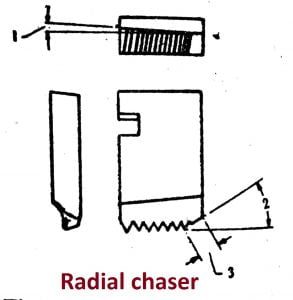
ii.Tangential chaser
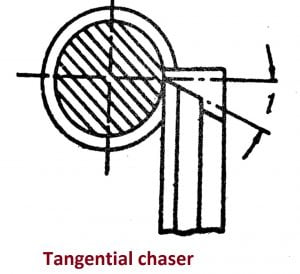
iii.Circular chaser
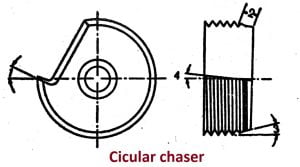
c. Single point tools

10. Internal thread cutting tool
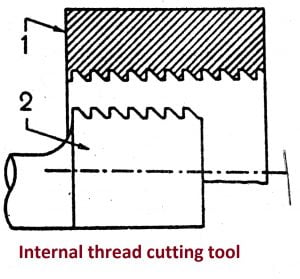
- The internal thread may be cutting in a capstan or turret lathe by using any one of the following tool:-
a. Solid tap
b. Collapsible tap
c. Single cutting tool or chaser
11. Chamfering tool

- The chamfering tool is mounting on the four-station turret on cross-slide.
- The extreme longitudinal position of the saddle is adjusting for the stop.
12. Workstop
- It is a cylindrical bar whose position can be adjusting relative to the spindle nose by the turret stop.
- In some workstops, micrometer graduations are provided for an accurate setting.

Work Holding Devices & Tool Holding Devices
| S.NO. | Work Holding Devices | Diagram | S.NO. | Tool Holding Devices | Diagram |
| 1. | jaw Chucks | 1. | Straight cutter holder | ||
| b. | Self-centering chuck |  | 2. | Multiple cutter holder |  |
| c. | Independent chuck |  | 3. | Offset cutter holder |  |
| d. | Combination chuck |  | 4. | Combination tool holder |  |
| e. | Air operated chuck |  | 5. | Knee tool holder |  |
| 2. | Collet chucks |  | 6. | Slide tool holder |  |
| a. | Push out type |  | 7. | Knurling tool holder |  |
| b. | Draw in type |  | 8. | Boring bar holder |  |
| c. | Dead length type |  | 9. | Recessing tool holder |  |
Comments
Well done sir..keep it up..
Thanks….
Figure are very interesting sir 🧐