Table of Contents
Introduction of Energy
- Energy is defined as the capacity to do work.
It is the fundamental property that enables systems or objects to generate motion, exert force, or produce heat.
Energy is present in everything that has the capacity to move or change.
- It can be converted from one from to another, but it cann’t be created or destroyed, only transformed.
- Energy is the word which comes from the Greek language.
- This is an ancient Greek word romanized from energeia operation.
- It was possibly appears in 4th century BC in the first time the work of Aristotle.
- Thomas Young was the first person who use the term “Energy” in modern sense in 1807.

- The source of energy is the Sun for most of life on the earth.
- The Sun derives its energy in the form of Nuclear fusion in its core.
- Energy is required for every living organism on the earth, without this human can not work without a single step.
- It is a scalar quantity.
- It has only magnitude but no direction.
Definition of Energy
- The ability to do work is called energy.
- Example- Cut a log of wood into small pieces, a moving cricket ball,etc,.
- There SI unit is joule which is denoted by J.
- Joule is the smaller unit.
- Kilo -joule is the bigger unit of Joule.
1 kilojoule =1000 J
1 kJ = 1000 J
- Joule is named on a British physicist James Prescott Joule.
Law of conservation of energy
- The law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted from one form to another, but it can’t be created or destroyed, only transformed.
- According to the 1st law of thermodynamic, this states that a closed system’s energy is constant unless it is transferred in or out by work or heat, and that no energy is lost in transfer.
Also read on touching the link:-
About related to machine click on the link
Types of Energy
- On the basics of mechanical energy, it is of two types:-
1. Kinetic Energy( KE )
2. Potential Energy( PE )
1. Kinetic Energy( KE )
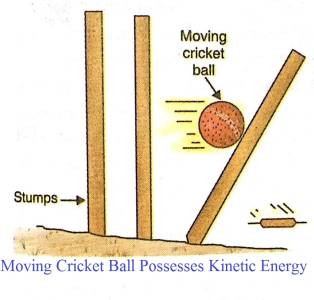
- The energy of a body due to its motion is term as KE.
- It means that a moving object can do work on another object when it strikes.
- For example- A moving cricket ball possesses KE, moving water, etc.
- The KE of a moving body measures from the amount of work it can do before coming to rest.
Formula
KE = ½× mv²
Here,
m = mass of the body
v = velocity of the body
From this formula, it clear that:-
i. The KE of a body is directly proportional to the mass of the body.
ii. The KE of a body is directly proportional to the square of the velocity of the body.
2. Potential Energy( PE )
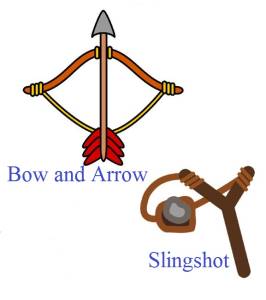
- The energy of a body due to its position or change in shape is known as PE.
- Scottish engineer and William Rankine was 1st the physicist who introduce the term PE in 19th century.
- PE associates with the forces that act on a body in a way that the total work done by these forces on the body depends only on the initial and final positions of the body in space.
- For example – A flying bird, a flying aeroplane, etc.
Formula
PE = mgh
Here,
m = mass of the body
g = acceleration due to gravity
h = height of the body above a reference point, say the surface of the earth
Source of Energy
- There are 13 best sources of energy : –
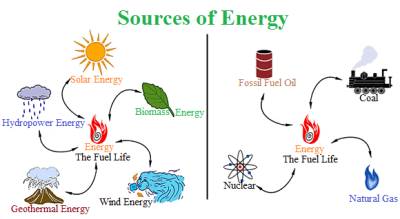
1. Oil
2. Coal
3. Uranium
4. Biomass
5. Fossil Fuels
6. Wood Fuel
7. Natural Gas
8. Wind Power
9. Solar Power
10. Tidal Power
11. Wave Power
12. Geothermal
13. Marine Current etc.
Types of Sources of Energy
- On the basics of sources, it can be divided into two types :-
1. Non – Renewable Sources
2. Renewable Sources
1. Non – Renewable Sources
- These are the sources of energy which are exhaustible i.e., cannot be replaced if once they are used.
- It is also know as conventional sources.
- This sources are dug out from the earth.
- They are present in a limited amount in the earth.
- For example – Oil, Fossil Fuels, Coal, Petroleum, Natural gas, Nuclear Fuels, etc,.
2. Renewable Sources
- These are the sources of energy which are inexhaustible i.e., can be used to produce it again and again.
- It is also know as Non – conventional sources.
- These sources can be used again and again.
- For examples:- Sun, Water, Animal dung, Agro- waste, Wood, Bio- gas, etc,.
A good source of energy would be one
- Which has high calorific value.
- Which is cheap and easily available.
- Be easy to store and transport.
- Eco -friendly.
- Less combustible.
- Which does not cause environmental pollution.
Forms of Energy
- They exist in many forms. The main forms of it are:-
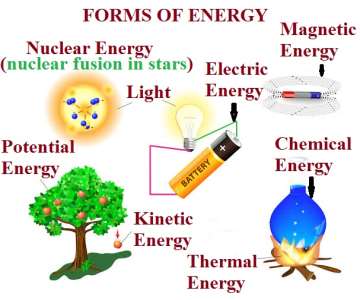
1. Kinetic Forms
2. Potential Forms
3. Chemical Forms
4. Electrical Forms
5. Thermal (Heat) Forms
6. Light Forms
7. Sound Forms
8. Nuclear Forms
1. Kinetic Forms( KE )
- The energy of a body due to its motion is term as KE.
- For example:- a moving cricket ball, shooting a rubber band, etc,.
2. Potential Forms( PE )
- The energy of a body due to its position or change in shape is known as PE.
- For example- Drawing a Bow, A Bird sitting at a height, etc,.
3. Chemical Forms
- It releases through a chemical reaction.
- Examples- gas stoves, water heaters, etc,.
4. Electrical Forms
- This is caused by moving electric charges called electrons.
- It is also a form of KE.
- Example- Solar, Fossil Fuels, etc,.
5. Thermal (Heat) Forms
- It is a form of energy transfer.
- It generates from the vibration of atoms and molecules within substances.
- They also know as Heat Energy.
6. Light Forms
- It is a form of electromagnetic radiation.
- It consists of photons, which are produced when an object’s atoms heat up.
- Light travels in the form of wave and it is the only form of vitality visible to the human eye.
7. Sound Forms
- It is the form of vitality that can be heard by humans.
- Sound is a mechanical waves and it produced when a force makes an object or substance vibrate.
- For Example- air and water, etc,.
8. Nuclear Forms
- It comes from the splitting of uranium atoms. This process is term as Fission.
- It creates heat to produce steam.
- Example- Nuclear Medicine, etc,.
Uses of Energy
- For lightning.
- To run the machines.
- In the field of transport.
- Its also used in the medical field.
- It used in the field for making food.
- For agricultural work and industrial activities.
Advantages and Dis advantages of Energy
| S.NO. | Advantages | Dis advantages |
| 1. | It is free. | Must be able to withstand. |
| 2. | It is renewable. | Expensive build. |
| 3. | They don’t expensive to operate and maintain. | Its hard to produce same amount. |
| 4. | There are no greenhouse gases. | Its harvesting is not appropriate for large scale. |
Let’s Know more
1. Define Calorific Value.
Ans:- The amount of heat generated by burning a unit mass of the fuel completely is know as its calorific value.
2. Define Fossil Fuel.
Ans:- A natural fuel formed deep under the earth from the pre- historic remains of living organisms is called a Fossil Fuel.

