Table of Contents
Solar Cell
- A solar cell is an energy conversion device that is used to convert sunlight into electricity by using the photovoltaic effect.
- That’s why it is also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell).
- It is usually made from silicon.
- A simple solar cell consists of sandwich of a ‘ silicon- boron layer ‘ and a ‘ silicion – arsenic layer ‘.
- The term Solar Cell designates to capture energy from sunlight, where PV cell is referred to an unspecified light source.
- The first practical solar cell was produced in 1954 using Selenium (Se).
- This solar cell could convert only 1% solar energy into electricity.

- Present day solar cells have efficiency as high as 25%.
- Now a days, Solar cells are usually produced from semiconductors, such as Silicon and Gallium.
- A single Solar cell produces very small current at a small potential difference.
- So, for practical use, a large number of such solar cells are connected together.
- A combination of a large number of solar cells is called a solar cell panel.
- Albert Einstein is known as the father of solar cells.
Solar Cell Definition
- A device which converts the sunlight directly into electricity is called a solar cell.
- Solar Cells are often coated with transparent thin film of silicon monoxide (SiO) to minimise the reflective losses from the surface.
Solar cells panel
- A solar cell panel can provide stronger currents under high potential difference.
- They use for producing electricity for use in space stations and artificial satellites.
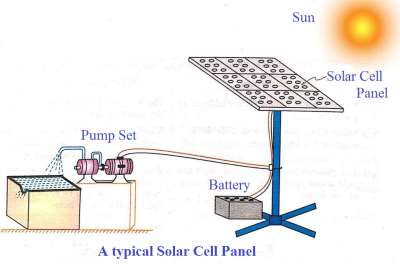
- They are very useful in remote and isolated locations.
- Solar cell panels are being used to produce electricity for:-
i. Street light in rural areas.
ii. Operating radio and TV sets.
iii. Lighthouses and offshore drilling rig operations.
iv. Operating water pumps for domestic and agricultural purpose.
Also read on touching the link:-
About related to machine click on the link
Solar Cell Materials
- There are 5 materials suitable for solar cell:-
1. Aluminum Silicon, Si ( 1.12eV )
2. Aluminum Antimonide, AlSb ( 1.27eV )
3. Cadmium Telluride, CdTe ( 1.5eV)
4. Zink Telluride, ZnTe ( 2.1eV )
5. Cadmium Sulphide, CdS ( 2.42eV ) etc. are the materials suitable for solar cells.
- The smaller the energy gap, the large number of photon of solar spectrum will be useful to produce the required energy for electrons to jump the forbidden band gap.
Working of Solar Cell
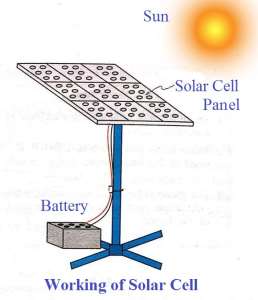
- Solar cell is an electric cell that converts sun’s electromagnetic energy into usable electrical energy.
- It is a semiconductor device and sensitive to photovoltaic effect.
- Solar cells normally consists of single crystal silicon P-n junction.
- When photons of light energy from the sun fall on semiconductor junction, the electron-hole pairs are created.
- Holes pass to the P– region and electrons pass to the N– region.
- The displacement of free charge creates an electric current when the load is connect across the terminals.
- This is the basic principle on which the solar cells work and generates power.
Note:
- Semiconductors are materials, which become electrically conductive when supplied with heat or light, but which operate as insulators at low temperatures.
Construction of Solar Cells
- In a solar cell, the pinnacle layer is present which includes an anti -reflective cover glass.
- This glass guards the semiconductor materials against the sunlight.
- In a solar cell, small grid patterns with slight metallic strips are available under the glass.
- So, that the top layer of cell can be formed by using the glass, metallic strips & anti- reflective coat.
- The most important part of this cell is the middle layer where solar energy can form through the effect of photovoltaic.
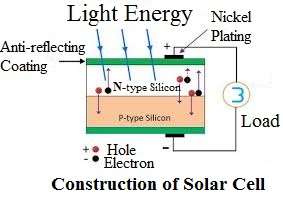
- They consist of two semiconductor layer which are made up of P- type and N– type materials.
- The base layer of the cell consists of two parts.
- A rear metallic electrode is beneath the P– type semiconductor and it works with the metallic grid to generate an electric current in the pinnacle layer.
- A reflective layer is the last layer in the cell which use to decrease the loss of light within the system.
Types of Solar Cells
- According to types of crystal, there are 3 types of solar cells:-
1. Mono crystalline silicon cells ( band gap 1.12 eV )
2. Polycrstalline silicon cells ( band gap 1.12 eV )
3. Amorphous silicon cells ( band gap 1.75 eV )
1. Mono crystalline silicon cells ( band gap 1.12 eV )
- In Mono crystalline silicon cells, silicon is dope with boron to produce P- type semiconductor.
- Mono crystalline rods are extracted from silicon and then sawed into thin plates or wafers.
![]()
- The upper layer of the wafers dope with phosphorous to produce N- type semiconductor. Then it becomes P-n junction.
- Maximum efficiency is 24%.
2. Polycrstalline silicon cells ( band gap 1.12 eV )
- In polycrystalline cells, liquid silicon pour into blocks that are sawed into plates.
- During solidification of the material, crystal structures of varying sizes are form.
- The size of crystallites mainly depends upon the cooling condition.
![]()
- If the molten silicon is cool very slowly, the crystallites of larger size are gain.
- The silicon solar cells made from polycrystalline silicon are low cost but low efficiency.
3. Amorphous silicon cells ( band gap 1.75 eV )
- It is the non- crystalline form of silicon used for solar cells and thin- film transistors.
- Its layer thickness is less than 1µ, so production costs are lower due to the low material costs.
![]()
- The efficiency of amorphous cells is much lower than that of the other cells.
- Maximum efficiency is 13%.
Solar Cell Properties
- Open circuit voltage (Voc)
- Short circuit current (Isc)
- Maximum power
- Efficiency
Factor affecting Solar Cell Performance
- Light intensity ( type of light)
- Light wave length (color of light)
- Angle of incident light
- Surface condition of solar cells (cleanness)
- Temperature on solar cells
Efficiency of Solar Cell
- The amount of power available from a PV device is determine by
– Its type and area of the material
– The intensity of the sunlight
– The wavelength of the sunlight
- The efficiency of single crystalline solar cells is 25%.
- The efficiency of Poly -crystalline silicon cell is less than 20%.
- Amorphous silicon solar cells is less than 10%.
- Cells are connect in series to form a panel to provide larger voltages and increased current.
Application of Solar Cells
- It is used for providing electricity in artificial satellites and space probes.
- It is used for operating water pumps for domestic and agricultural purposes.
- It is used for street lighting in rural areas.
- It is used for operating radio and tv sets in remote/ rural areas.
- It is used for providing electricity to light houses and offshore drilling rig operations.
- It is used for operating traffic signals, watches, calculators and toys.
- Its may be use in the field of emergency power.
Advantages of Solar Cell
- It is a renewable source of energy.
- Its free of charge.
- It doesn’t cause pollution.
- They can be use in remote areas.
- The system has long life of 10- 15 years or more.
- The energy cost is very low because the sources are available freely.
- More Solar energy in summer.
Dis advantages of Solar Cell
- It needs lots of space.
- High initial cost.
- No Solar power at night & cloudy days.
- Less Solar energy in winter.
- DC equipment are expensive.
Let’s Known More
1. What is a solar heater?
Ans:- A solar heater is a device which is use for heating water by utilising the heat energy of the sunlight.
2. What is the Solar heating device?
Ans:- A device which is use for collecting heat radiation of the sunlight in a small region is term as a solar heating device.
3. Name any two components of solar radiation that are not visible to us.
Ans:- The two components of solar radiation that are not visible to us are:
i. Infrared radiation
ii. Ultraviolet radiation
4. What is Solar energy?
Ans:- The light and heat energies of the sunlight are collectively term as a Solar energy.
5. What are the traditional applications of solar energy?
Ans:- i. For drying clothes
ii. For making salt from sea
iii. For reducing the moisture content of food grains
iv. For sun- drying of vegetables, fruits, fish, etc.
6. What is Solar cell panel?
Ans:- A combination of a large number of solar cells is term as a Solar cell panel.
7. What are Semiconductors?
Ans:- Semiconductors are the materials which ordinary do not allow electricity to flow through them.
- It’s mean that it is not good conductor of electricity.
8. What are the application of solar thermal energy?
Ans:- i. Its use in the field of powering earth satellite.
ii. They also use in the field of solar water heating.
iii. Its also use in the field of electric power generation.
iv. Its may use in the field of solar distillation.
v. They may use in the field of solar domestic cocking.
9. Define Concentrating Collector.
Ans:- It is a device to collect solar energy with the high intensity of solar radiation on the absorbing surface with the help of reflector or refractor.


