Boiler | Definition, Principle & Working, Properties, Classification &Component
Boiler A boiler is a container in which water is heated to produce steam in an engine. It is constructed…
Table of Contents
Boiler
- A boiler is a container in which water is heated to produce steam in an engine.
- It is constructed of steel or iron, where water is converted into steam by the application of heat.
- It means that it is a pressure vessel in which steam is generated wholly or partly under pressure.
- It includes valves, gauges, fittings, controlers, etc., which are called accessories.
- George Babcock and Steven Wilcox were the first people to paint a boiler design.
- It was first invented in the 17th century, and at that time, boilers and steam engines were prime movers for pumping water from deep coal mines as well as the industrial revolution.
- It doesn’t add humidity to the air.
- Today’s new boiler can reduce heating costs by 90% and use inexpensive as well as green energy.
- Its low water pressure can also sabotage radiant heating systems.
Schematic diagram of Boiler
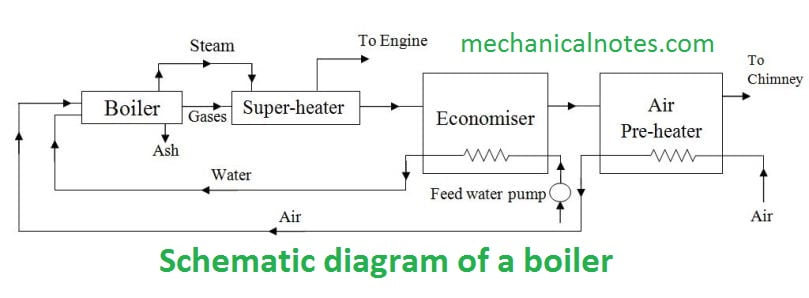
Definition of Boiler
- A boiler is a closed pressure vessel strongly constructed of steel or iron where water is converted into steam by the application of heat.
Efficiency
- The efficiency of a boiler may be defined as the ratio of amount of steam generated per hour to the amount of heat supplied by the fuel per hour.
Efficiency ( η ) = ( Heat Output / Heat Input ) × 1oo
→https://mechanicalnotes.com/cochran-boiler-definition-main-parts-working-features-advantages/
Principle & Working of Boiler
Principle
- The main basic principle of the boiler is to convert water into steam by applying heat.
- This steam is super heated.
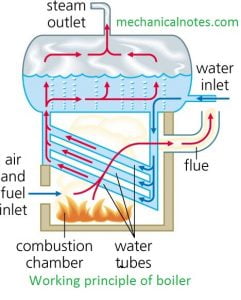
Working
- The workings of a boiler are very simple and easy to understand.
- As we know, a boiler is a closed vessel where water is stored first.
- Fuel is burned in a furnace, and water is converted into hot gases.
- These hot gases come into contact with water vessels, where the heat of such gases transfers to the water.
- Hence, steam is produced in the boiler. This steam is superheated.
- Thus, this steam is piped to the turbine of a thermal power plant, where it is used for different purposes, like running a production unit.
Properties of a good boilers
- A good boiler produces the maximum quantity of steam with the minimum fuel consumption.
- It should have sufficient safety interlocks and be simple to disassemble.
- It should start and stop quickly, and installation should be simple.
- Every component must be accessible for cleaning and inspection.
- According to the boiler, check the location of the process plant.
- It should have good availability of water and quality.
- On heating surfaces, scaling should not take place.
- It should use less floor area and vibrate less.
- It should have a high rate of combustion.
- It should have good operating pressure.
- It should have low maintenance costs.
- It should have a low initial cost.
Selection of Boiler
- Selection of boiler is based on its operating pressure(psig) and steaming capacity( Lbs/Hr).
- It should be selected on the basis of its uses, either making steam or hot water.
- It should be selected on the basis of steam generation rate.
- It should be selected on the basis of system design.
- Accessibility for repair and inspection is required.
- It should be selected based on comparative initial cost.
- It should be selected based on fuel and water availability.
- It should be selected based on portable load factor.
- It should be selected based on erection facilities.
- It should be selected based on operating and maintenance costs.
Classification of Boiler
The boilers may be classify mainly on the basis of the following parameters:
1. Axis of the shell
a. Vertical
b. Horizontal
c. Inclined
2. Use of boilers
a. Stationary
b. Portable
3. Tube contents
a. Fire tube
b. Water tube
4. Furnace position
a. Externally fired
b. Internally fired
5. Method of water circulation
a. Natural circulation
b. Forced circulation
1. Axis of the shell
a. Vertical
- If the axis of the boiler is vertical then it called as vertical boiler.
- It’s occupy less floor space.
b. Horizontal
- If the axis is horizontal than it called as horizontal boiler.
- The pieces of a flat evaporator can be reviewed and fixed effectively yet it consumes more space.
c. Inclined
- If the axis is inclined than it called as inclined boiler.
2. Use of boilers
a. Stationary
- Stationary boilers are utilized for power plant steam for focal station utility force plants, for plant process steam and so on.
b. Portable
- Portable boilers are portable and are of small size.
- For example:- Locomotive and Marine boilers.
3. Tube contents
a. Fire tube
- In fire tube boilers, the hot gases are inside the tubes and the water surrounds the tubes.
- For example:- Cochran, Lancashire and Locomotive boilers etc.
Fire tube boilers are:
- Relatively inexpensive.
- Easy to replace tubes.
- Easy to clean.
- Compact in size.
- Available in size from 600,000 btu/hr to 50,000,000 btu/hr.
- Appropriate for space warming and modern procedure applications.
Disadvantages
- Limitation for high capacity steam generation.
- Not appropriate for high weight applications 250 psig or more..
b. Water tube
- In this case of water tube boiler, the water is inside the tube and hot gases surround them.
- For example:- Babcock and Wilcox, Stirling, Yarrow etc.
Water tube boilers:
- Faster recover than their fire-tube cousin.
- They have ability to reach very high temperatures.
- They are able to handle higher pressures upto 5,000 psig.
- It’s available in sizes far greater than a fire tube design, up to several million pounds per hour of steam.
Disadvantages
- High initial capital cost.
- No commonality between tubes.
- Phsical size may be an issue.
- Cleaning is more difficult due to the design.
4. Furnace position
a. Externally fired
- The boiler is known as externally fired if the heat addition is done externally i.e. furnace is outside the unit.
- For example:- Babcock & Wilcox etc.
b. Internally fired
- In case of internally fired boiler, heat addition is done internally i.e. furnace is within the unit.
- For example:- Cochran and Lancashire.
5. Method of water circulation
a. Natural circulation
- In natural circulation boilers, the circulation of water/steam is caused by the density difference which is due to the temperature variation.
- For example:- Lancashire
b. Forced circulation
- In constrained dissemination sort of boilers, the flow of water is finished by constrained siphon.
- For example:- Velox, Lamont etc.
10 Basic components of Boiler
- Furnace
- Economiser
- Air -Preheater
- Super heater
- Re – heater
- De -Super heater
- Condenser
- Cooling tower
- Fan or draught system
- Ash handling system
Applications of Boiler
They having a very wide application in different industries such as
- Power Sector
- Thermal Power Plants
- Sugar Plants
- FM CG
- Food Processing Industries etc
Thanks for reading. If the articles help you then please spread your love and don’t forget to share it on social network’s.
Comments
Osom the way of writting and attraction site.
Thanks…mechanicalnotes.com
Thanks…