Table of Contents
Networking Introduction
- Networking is referred as connecting computers electronically for the purpose of sharing information such as files, applications, etc.
- Basically, network consists of hardware component like computer, hubs, switches, routers and other devices which form the network infrastructure.

- These are the devices that play an important role in data transfer from one place to another using different technology like radio waves and wires.
- A network may be linked through cables, telephone lines, radio, satellites, or infrared light beams.
- It interact with others to exchange information and develop professional or social contacts.
Definition of Networking
- A network consists of two or more computer that are linked in order to share resources, exchange files, or allow electronic communication.
or
- Network means connect the people across the globe and share their idea’s and thought’s.
Components of Networking
- Following are the components of Network :-
1. Network Card
2. Networking Cable
3. Hubs and Switches
4. Modem
1. Network Card
- A network card is used to physically attach a computer to a network, so that can participate in network communication.
- In network card Ethernet Network Card is the most commonly used.
2. Networking Cable
- A Networking cables are networking hardware’s use to connect one network to other network devices and to connect two or more computers to share scanners, printers etc.
3. Hubs and Switches
- A Hub is a networking device that allows one to connect multiple computers to a single network.
- They may be based on Ethernet, Fire wire, or USB connections.
- A switch is a control unit which turns the flow of electricity on or off in a circuit.
- They may also be use to route information patterns in streaming electronic data sent over networks.
- A Hub/Switch performs the following functions :-
- Acts as a central points of connection for all the computers on a network. Every computer plugs into the hub/switch.
- To arrange the points in such a way, so that if a PC transmits data, the data is sent over the other computer through its network card.
- Basically, the hub/switch is a box with a set of RJ-45 ports. Each computer on a network is connect to the hub/switch via Ethernet cable.
4. Modem
- A modem enables you to connect your PC to the available internet connection over the existing telephone lines.
- It converts the digital signals of a PC into analog signals to enable their transmission via phone lines.
Types of Networks
- There are various types of networks which are as follows :-
1. Personal Area Network ( PAN)
2. Local Area Network ( LAN )
3. Metropolitan Area Network ( MAN )
4. Wide Area Network ( WAN )
1. Personal Area Network ( PAN)
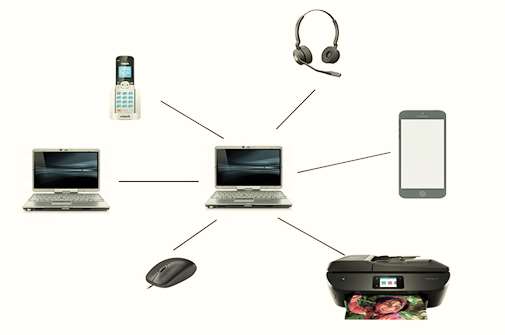
Image: PAN
- PAN is a PC network that’s mainly created for an individual person.
- This is used for communication among devices, like laptops, mobile phones, PDA or smartphones.
- PAN generally covers a range of less than 10 meters ( about 30 feet ).
- They may be wired or wireless.
2. Local Area Network ( LAN )
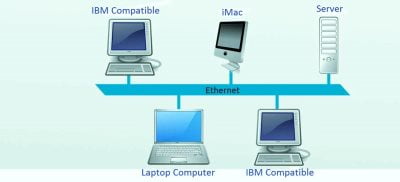
Image: LAN
- In LAN, two or more computers and peripheral devices are connected within a small area, like room, office building or a campus.
- In Local Area Network, computer terminals are physically connected with wires.
- The data transmission speed is slow as compared to Wide Area Network.
- Since LAN is operated in a small area, it can be controlled and administered by a single person or an organisation.
3. Metropolitan Area Network ( MAN )
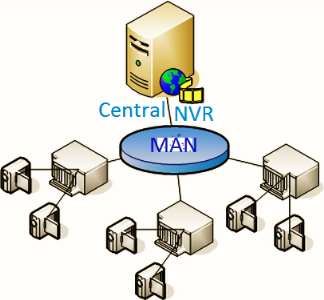
Image: MAN
- MAN is large network than LAN.
- It spreads across a city.
- Since it covers a city, which is called metropolitan.
- The most common example of Metropolitan Area Network type network is the cable television, branches of a local bank in a city, etc.
4. Wide Area Network ( WAN )
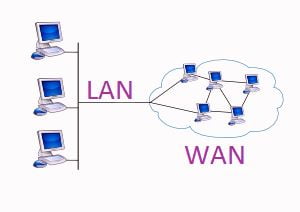
Image: WAN
- In WAN network connects two or more computers located at distant places.
- They link to communicate facilities, like telecommunication or satellite signals for example telecom system, ATM facility, etc.
- The main characteristic of Wide Area Network is that it requires a public telecommunication media to transfer data.
Networking Architecture
- Network architecture is overall design of a computer network that describes how a computer network is configured and what strategies are being used.
- Network architecture mainly are of two types, which are as follows :-
1. Client- Server Network
2. Peer to Peer Network
1. Client- Server Network
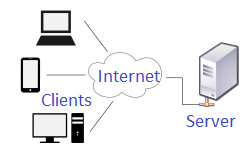
Image: Client- Server Network
- This is a network, where several computers called Clients or workstations are connected to the main computer called the server.
- A Server is a computer which provides services to clients and controls access to hardware, software, and other resources.
- Clients are the computers, that request services, like data retrieval, storage, etc., from the server.
2. Peer to Peer Network
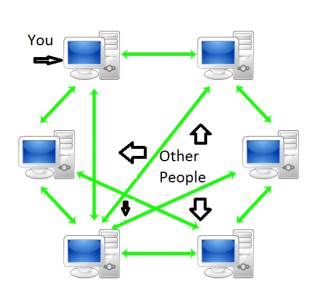
Image: Peer to Peer Network
- This is a network where a few computers having equal capacity and capabilities are connected together to use the resources available on the network.
- In this network, there is no central server instead each computer can act as a server as well as a client.
Network Topologies
- Network Topology refers to the layout in which various components of a network, like nodes, links, peripherals, etc, are connected and communicate with each other.
- Topology can be either physical or logical.
- Physical Topology is the physical format of nodes, workstations and cables in the network.
- Whereas Logical topology is the way information flows between different components.
- Network Topologies are classify into the following basic types :-
1. Point- to- Point
2. Bus Topology
3. Star Topology
4. Ring Topology
5. Tree Topology
6. Mesh Topology
1. Point- to- Point

- This is the simplest form of networking structure in which two nodes are directly connected to each other.
- This type of network is more suitable for small areas where computers are in close proximity.
- This technology provides a faster and reliable connection.
2. Bus Topology
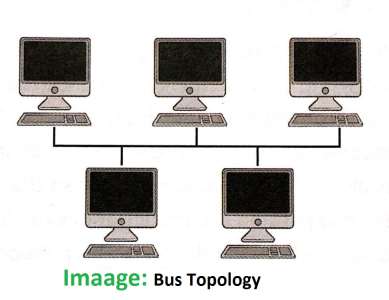
- This topology uses a single communication line or one main cable to which all nodes are directly connected.
- The main cable acts as a backbone for the networks.
- In this type of structure one of the computers in the network acts as the computer server, that provides data to all the clients.
- This topology uses in small networks where cable requirement is relatively small.
Di advantages
- If the main cable fails, the entire network becomes unusable.
- For this reason, this type of topology is not using for large networks.
3. Star Topology
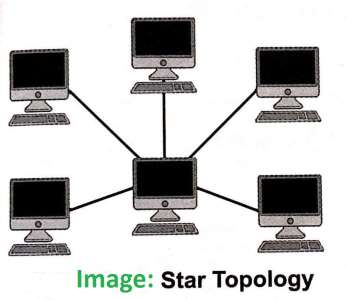
- In this topology, each device connects to a central computer using a point- to- point connection. The Central server acts as a Hub.
- This is very popular because the startup cost is low.
Advantages
- If any one connection in the network fails, the other connections remain intact.
Di advantages
- If the central hub fails, the entire networks go down.
4. Ring Topology
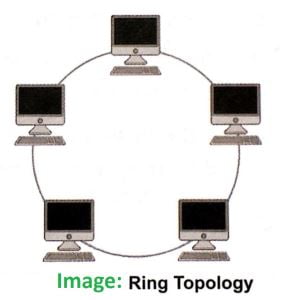
- In this topology, all the nodes in the network connects in a circular manner.
- Each nodes connect to exactly two other nodes, forming a single continuous pathway for signals.
- Both LAN & WAN setups are use in Ring topology.
Di advantages
- If one workstation goes down, the entire networks got affect.
5. Tree Topology
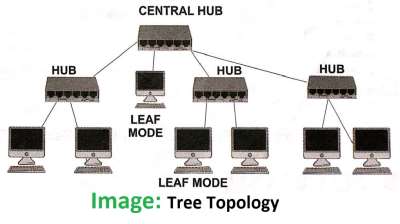
- This is one of the most common network setups that consists of a group of star- figured workstations connected to a linear bus backbone cable.
- In this topology, one star network connects to the other star networks.
- In a tree network, a cable failure in one of the star network will isolate only the workstation that links to the central computer of that star network.
- Whereas, all the other workstations will continue to function normally.
- If central computer goes down, the entire workstations connect to it will suffer either degrade performance or complete failure, but rest of the network will continue to function normally.
- In the Tree topology, expansion of network is possible and easy but maintenance becomes difficult.
6. Mesh Topology
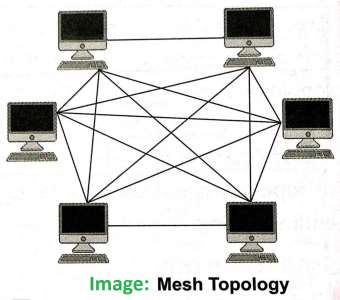
- In this topology, each node connects to every other node in the network.
- In Mesh topology, every node not only sends its own signals but also relays data from other nodes.
- This type of topology can handle a large volume of traffic.
- In case, if one of the component fails, there is always an alternative present so that the data transfer doesn’t get affected.
- Even expansion and modifications can be done in this topology without affecting other nodes.
- Overall cost of this network is extremely high as compared to other network topologies.
Networking Security
- Networking Security means protecting data and resources from any unauthorised access.
- It is the most important aspect in computer networking.
- These are the following points that may happen in any organisation :-
- Some employees may try to change the data concerning their leave records, salaries, performance appraisals, etc.
- Accidental deletion of important data.
- Former employees or some other people may try to harm the company’s data.
- People outside the company can try to access confidential data.
- There are Two general levels of networking security :-
1. Login security
2. Right security
1. Login security
- You give a unique login name and password.
2. Right security
- Based upon your user name, you give rights, like Read- Only Access or Read- Write Access at all.
- A combination of rights may also be granted to the same user for different sets of data.
Advantages of Networking
- For efficient use of storage media.
- For preserving information.
- To reduction in hardware costs.
- Efficiency
- For redundancy
- Quickest document delivery
Dis advantages of Networking
- A PC on a network is vulnerable to hackers.
- There is a chance of hacking, particularly with wide area networks.
- Viruses can spread to other computers throughout a PC network.
- If the file server breaks down the files on the file server become difficult to reach.
Application of Networking
- For sharing.
- Printer sharing.
- To Communication and collaboration.
- To remote access.
- For data protection.
About related to machine click on the link
Let’s Know More
- Conferencing
- When two users have simultaneous conversation via internet, it’s call Conferencing.
- Video Conferencing
- In Video Conference participants in different locations are able to communicate with each other in sound and vision.
- Bluetooth
- It is a wireless technology use for interconnect mobile phones, computers, printers using short- range of wireless connection.
- Protocols
- Protocols are the certain sets of rules that determine how data should be transfer over the screen and so on.
- Wireless
- It means of communication that uses low power ratio between devices.
- Wi-fi
- Wi-fi stands for Wireless Fidelity.
- It represents wireless local area network.
- WAP
- WAP stands for wireless access point.
- This is a device that connects wireless communication devices to form a wireless network.
External Link
